LY5B lamp with illustrated light center and rays
Light center length of automotive LED lamps
Application Note - Measurement of the light center length of automotive LED lamps according to IEC 60809:20211
This page shows a summary of the application note. Topic of the document is the measurement of the light center length based on the example of an LED signal lamp of type LY5B using a near-field goniophotometer of type RiGO801 - LED. The method based on the evaluation of ray data is specified in the IEC 60809:2021 [1] standard.
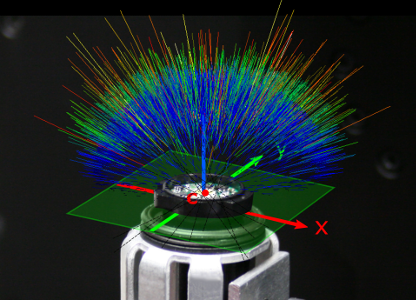
Measurement of ray data with the near-field goniophotometer RiGO801 - LED
All RiGO801 goniophotometers are based on the near-field measurement principle. A luminance measurement camera captures the complete spatial luminance distribution of a light source. From these data, ray data and luminous intensity distribution are derived based on the photometric fundamental law (see [2], [3], [4], [5], [6]).
Ray data (also ray file) is a data set of vectors with associated luminous flux components. A sufficiently high number of rays accurately represents the complete light source distribution pattern. The ray data are processed with the free software Converter801. In addition to exporting the data to all common file formats, various evaluations can be performed, e.g. calculation of the center of light or of the photometric center.
The goniophotometer type RiGO801 – LED is specially designed for the measurement of ray data of LEDs and LED modules. The luminance measuring camera LMK 6-5 is moved on a circular arc (theta-axis) around the measuring object mounted on the standing rotation axis (phi-axis).
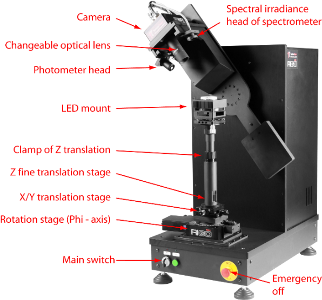
RiGO801 - LED
Measurement of the light center length according to IEC 60809:2021
Annex K.1 of IEC 60809:2021 describes a method for measuring the light center length for LED lamps of types Lx3A, Lx3B, Lx4A, Lx4B, Lx5A, Lx5B8), L1A/6 and L1B/6.
The light center length is calculated from measured ray data. The light center is defined as the location where the sum of the quadratic distances of the ray vectors is minimum.
By using the coordinate system aligmnent feature of the RiGO801 measuring software, the lamp is positioned as given in the standard. The measuring resolution is set to 1° x 1°.
Results
The measured TTR ray file is opened with the Converter801 program. The algorithm for calculating the light center is run from the menu item Tools -> Calculate the center of gravity of rays. According to IEC 60809:2021, 1 million rays is sufficient.
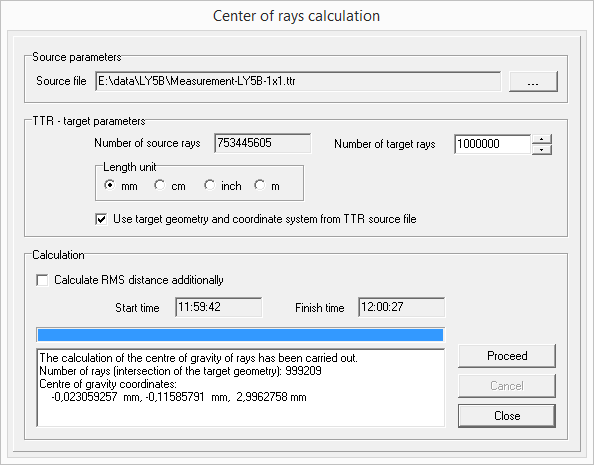
Dialog for calculating the light center coordinates
The result is displayed in the output window. The center of light length e is here the Z coordinate of the light center. The result is e = 2.996 mm. According to R.E.5 [7], the tolerance is +/- 0.3 mm for "Production LED light sources" and +/- 0.15 mm for "Standard LED light sources". Tolerances for the similarly calculated x and y coordinates of the light center are not listed in the standards. Here they are very close to the symmetry axis of the lamp with -0.02 and -0.12 mm.
Summary
In this Application note, it was shown how to determine the light center length of an automotive signal lamp from ray data in accordance with the requirements of IEC 60809:2021 with little measurement effort. Many practical tips were given and possible sources of error in the measurement or processing of the ray data were explained.
The near-field goniophotometer RiGO801 - LED is very well suited for the measurement task. The measuring time at a high angular resolution of 1° x 1° is very short due to the continuous on-the-fly measurement and therefore suitable for practical use. The measurement method has already proven itself many times in the industry.
Download
References
| [1] | IEC 60809:2021, „Lamps and light sources for road vehicles - Dimensional, electrical and luminous requirements,“ IEC, 2021. |
| [2] | CIE 070-1987, „The Measurement of Absolute Luminous Intensity Distributions,“ CIE, 1987. |
| [3] | R. Poschmann, M. Riemann und F. Schmidt, „Verfahren und Anordnung zur Messung der Lichtstärkeverteilung von Leuchten und Lampen“. DE Patent 41 10 574, 30 March 1991. |
| [4] | M. Riemann und F. P. R. Schmidt, „Zur Bestimmung der Lichtstärkeverteilung von Leuchten innerhalb der fotometrischen Grenzentfernung mittels eines bildauflösenden Goniofotometers,“ LICHT, Nr. 7-8, pp. 592 - 596, 1993. |
| [5] | I. Ashdown, „Near-Field Photometric Method and Apparatus“. USA Patent 5,253,036, 12 October 1993. |
| [6] | I. Ashdown, "Near-field photometry: a new approach," J. Illuminating Engineering, vol. 22, pp. 163-180, 1993. |
| [7] |
Resolution (RE5), „Consolidated Resolution on the Common Specification of Light Source Categories (RE5).,“ ECE - United Nations. |


